Migration from MariaDB to PostgreSQL
Introduction
This guide describes the process of migrating the database for a Relution instance within a Docker environment.
Prerequisites
Before starting the migration, ensure the following conditions are met:
- Disk Space: At least as much free space as the current MariaDB database size (1:1 ratio).
- S3 Storage: MinIO (or a compatible S3 storage) must be configured.
deprecated Documentation for S3/MinIO. - Version: The Relution instance should be updated to version 26.0.0, but at least to version 5.31.0.
Data Backup (Optional)
If no virtual machine snapshots or external backups are available, perform a manual export and file backup.
Export MariaDB to a SQL file:
docker exec docker_mariadb mariadb-dump -u relution -p --max_allowed_packet=5G relution > relution.sql
Backup configuration files:
cd /opt/relution/ && zip -r backup.zip ./*
Prepare the Environment
Update Relution
Ensure you are running the latest version:
cd /opt/relution/ && docker compose pull && docker compose up -d
Stop Services
Stop the Relution container to ensure data consistency during preparation:
docker compose down relution
Modify Docker Configuration
Update your docker-compose.yml. Add the services for pgloader and the new database (PostgreSQL), and adjust the relution block.
Add New Services
services:
pgloader:
image: dimitri/pgloader:latest
networks:
- relution-network
volumes:
- "./pgloader.load:/pgloader.load"
tty: true
database:
image: postgres:18
restart: unless-stopped
container_name: database
environment:
- TZ=Europe/Berlin
- POSTGRES_DB=relution
- POSTGRES_USER=relution
- POSTGRES_PASSWORD=$PASSWORD
expose:
- "5432"
volumes:
- "postgresql:/var/lib/postgresql"
networks:
- relution-network
Adjust Existing Relution Block
Change the dependencies and add the migration argument:
relution:
image: relution/relution:latest
restart: on-failure # Changed from always to on-failure
container_name: docker_relution
networks:
relution-network:
aliases:
- relution-docker
depends_on:
- database # Changed from mariadb
links:
- database # Changed from mariadb
environment:
- TZ=Europe/Berlin
- RELUTION_ARGUMENTS='--database-migration-only' # Newly added
volumes:
mariadb:
postgresql: # Newly added
pgloader Configuration
- Download the file pgloader.load into the directory
/opt/relution/ - Adapt the configuration to match your environment.
FROM mysql://relution:dbpassword@mariadb-docker:3306/relution
INTO postgresql://relution:dbpassword@database:5432/relution
Initialize Database Schema
First, adjust the application.yml so that Relution recognizes the shift to PostgreSQL:
relution:
database:
type: postgresql
url: jdbc:postgresql://database/relution?useServerPrepStmts=true
username: relution
password: $PASSWORD
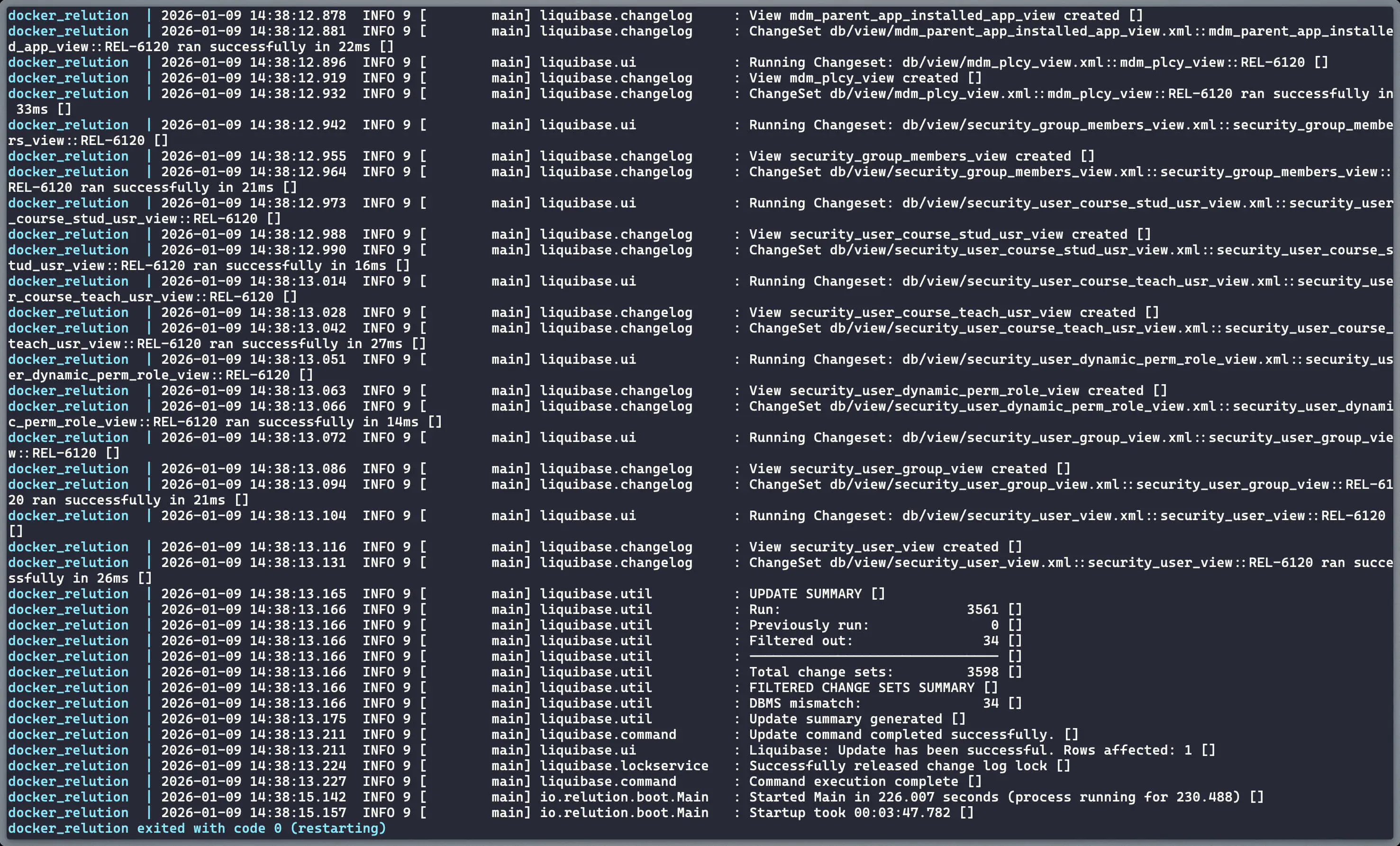
Now start PostgreSQL and Relution. Due to the --database-migration-only flag, Relution will only create the schema in PostgreSQL and then terminate.
docker compose up -d database && docker compose up relution
The process is complete when the container exits with code 0:
docker_relution exited with code 0
Execute Data Migration
Start the pgloader container and migrate the data from MariaDB to PostgreSQL:
docker compose up -d pgloader && docker compose exec pgloader bash
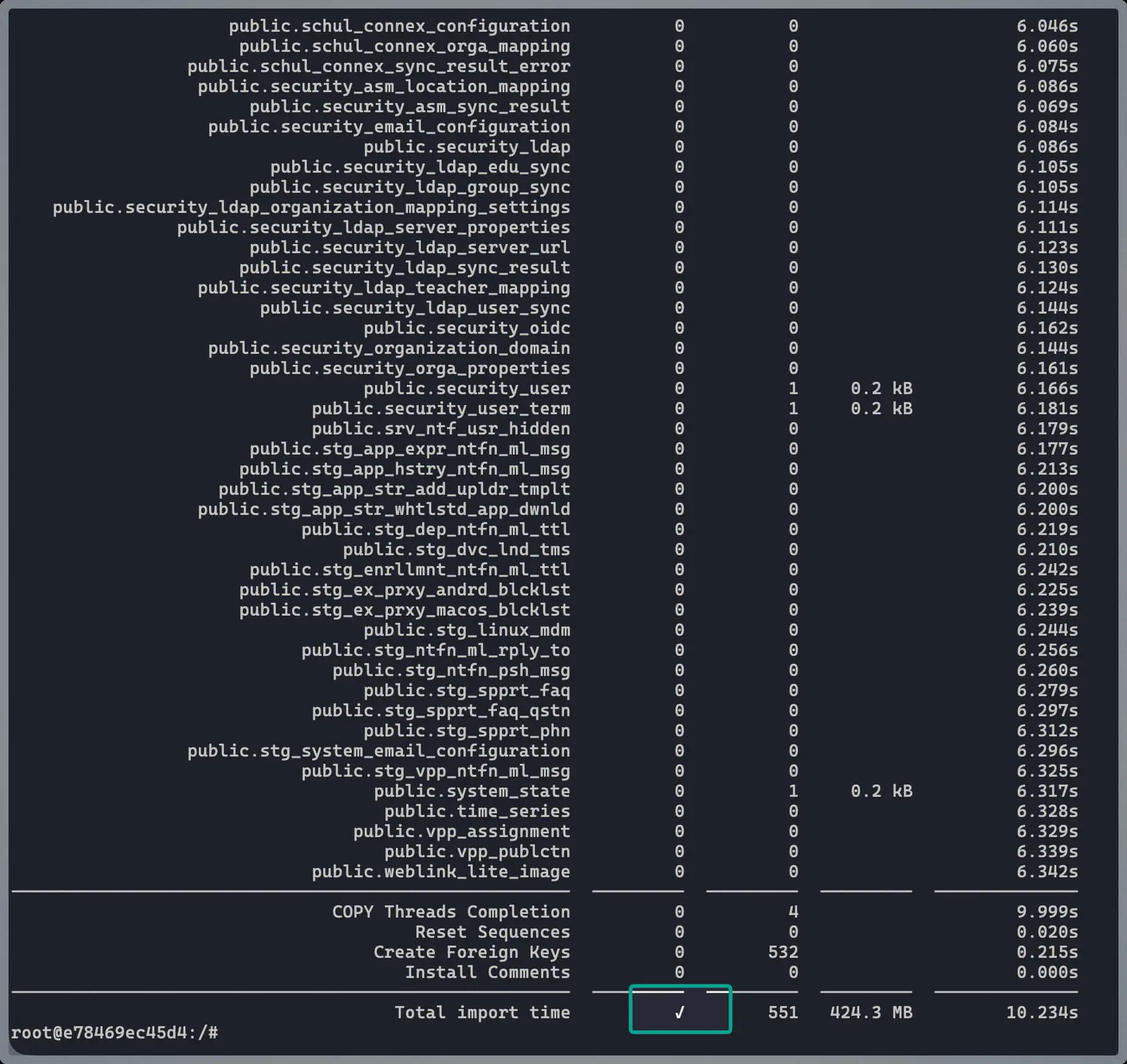
Inside the container, run the migration command:
pgloader pgloader.load
Cleanup and Completion
After a successful migration, the temporary configurations and the old MariaDB container must be removed.
- Remove from
docker-compose.yml:
- The entire
mariadb:block underservices. - The
pgloader:block underservices. - The
mariadb:volume undervolumes.
- Adjust the
relutionblock:
- Change back from
restart: unless-stoppedtorestart: always. - Remove the line:
- RELUTION_ARGUMENTS=--database-migration-only.
- Delete migration file:
rm pgloader.load
Restart Services: Shut down everything to remove orphaned containers and restart the system:
docker compose down --remove-orphans && docker compose up -d
The migration is now complete, and Relution is running natively on PostgreSQL.